SHA1 hash:
- 231ebce457fb9c1ea23678e25b3b62b942febb7d (cef2.exe)
Description
A trojan app written in the C++ programming language and designed to run on computers with Microsoft Windows. It downloads and launches the malicious downloader script Python.Downloader.208 on target devices.
Operating routine
When launched, Trojan.DownLoader48.54600 deletes all of the files in the directory %TEMP% and verifies whether it was launched from the directory AppData.
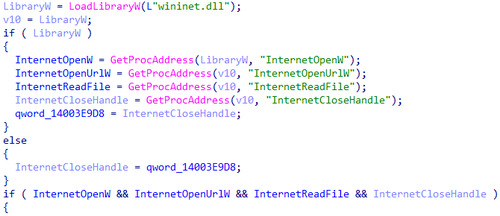
Next, it dynamically loads the Windows API library wininet.dll and uses the function GetProcAddress to obtain the addresses of the API functions InternetOpenW, InternetOpenUrlW, InternetReadFile, and InternetCloseHandle.
Dynamically obtaining the addresses of the API functions
During the next step, it tries to create directories for storing the payload from the downloaded archive python3.zip. It also initializes the key strings \\python3[.]zip, \\svpy[.]exe, and \\maintaindown[.]py to prepare the payload to be launched after its extraction.
Creating a directory and initializing the strings
In the function create_dir, Trojan.DownLoader48.54600 tries to obtain the path to the directory %LOCALAPPDATA%, using the function SHGetKnownFolderPath and the parameter FOLDERID_LocalAppData.
If successful, it creates a new directory in %LOCALAPPDATA%. Its name is formed from a random number that is concatenated with the prefix t.
If it is unable to obtain the path to the directory %LOCALAPPDATA% via the function SHGetKnownFolderPath, further operations will be performed in the directory C:\Users\Public\Temp.
For downloading the archive, Trojan.DownLoader48.54600 decrypts the following URL in real time: hxxps[:]//down[.]temp-xy[.]com/update/python3[.]zip. For the decryption, it uses a self-made XOR with the constant 0xA.
Decrypting the URL for downloading the target archive
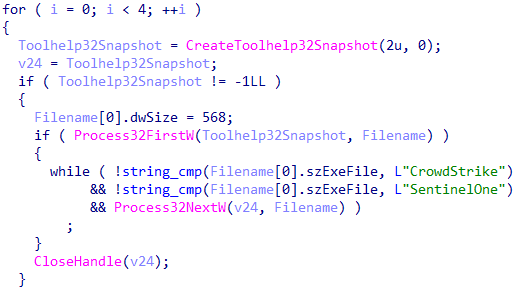
The trojan makes 4 attempts to download the target file, and each time, for an unknown purpose, it tries to locate processes from the CrowdStrike and SentinelOne programs.
Searching the CrowdStrike and SentinelOne processes
Right before downloading the file, Trojan.DownLoader48.54600 tries to determine whether it was launched in an artificial environment. For this, it checks the available RAM (there must be at least 2 gigabytes) and measures the execution time of the function Sleep to detect speedups, which are typical for debugging environments. It also verifies the number of records in the system event log (there must be at least 120 entries). If the trojan detects any sign of a debugging environment, it deletes all of the files in the directory %TEMP% and terminates.
Verifying the execution environment prior to downloading the target archive
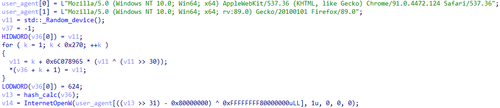
If the anti-debugging check is successful, Trojan.DownLoader48.54600, based on the class Random_device and custom hashing, randomly selects one of two possible user-agents: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 or Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:89.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/89.0.
Randomly selecting the user-agent
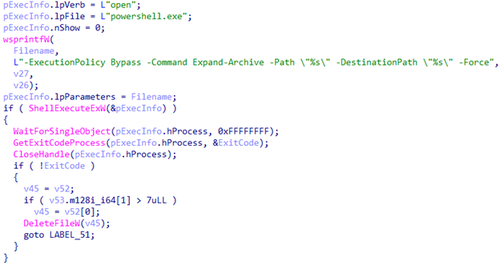
Next, it uses the previously decrypted address to download the target archive from the C2 server. The contents of this archive are extracted via the PowerShell command Expand-Archive, and the archive is then deleted.
Unpacking the archive, using PowerShell
The file maintaindown[.]py extracted from the archive is a Python script (the malicious downloader Python.Downloader.208). This script is launched by Trojan.DownLoader48.54600 via the function CreateProcessW.
Running the malicious Python script, extracted from the archive
To finish up, Trojan.DownLoader48.54600 creates the file tmp.bat, which is used to delete all of the files related to the trojan.
More details about Python.Downloader.208